Enlarged Breasts in Men (Gynecomastia), develop when the male breast tissue develops in size as a result of hormonal imbalance. It is a non-cancerous (benign) condition, which can result in emotional distress or physical tenderness. It could present itself in one or both breasts, and it is present in males of all ages span: newborns to elderly. Learning the causes, symptoms, and treatment of it will assist the men in making informed health choices.
Key Takeaways
- Gynecomastia is a benign tumor of the male breast due to hormonal imbalance between the estrogen and the testosterone hormones.
- It is normal and can be temporary, although chronic ones can be treated either medically or surgically.
- Prevention or minimization of recurrence is through healthy lifestyle habits that include avoiding alcohol, steroids, and some medications.
- Timely medical assessment will make sure that it is well diagnosed and is treated effectively with confidence.
What is Gynecomastia?
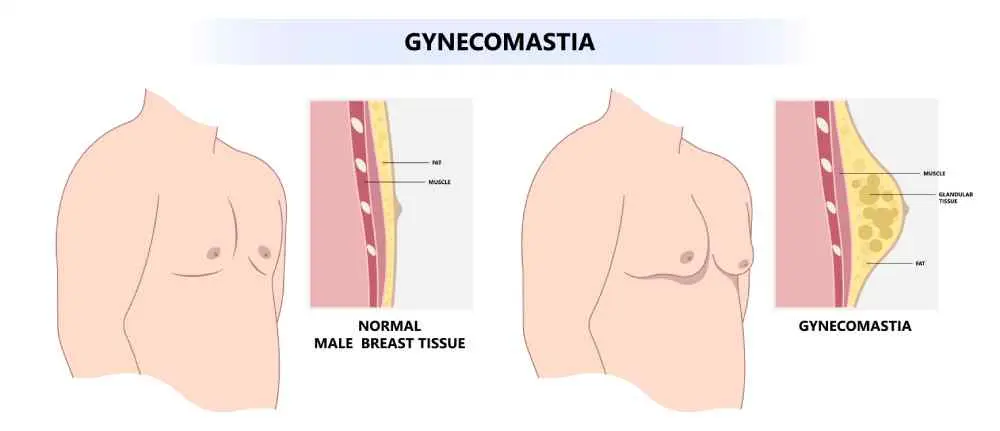
Gynecomastia refers to the excessive growth of glandular breast tissue in the male body and not merely fat build-up. It is caused by the disequilibrium between estrogen and testosterone with the preponderance of the former. The condition is widespread, and may be both transient and chronic, depending upon its cause. Even though it is not dangerous, it can impact the confidence and body image.
Why Does Gynecomastia Happen?
In cases where estrogen levels go up or decreased testosterone levels, gynecomastia develops. It can be caused by hormonal changes in puberty, old age, or some diseases. Of course, so do drugs such as anabolic steroids, antidepressants, and anti-androgens. In other instances, it is caused by alcohol, marijuana or liver disease.
Common causes include:
- Endocrine (low testosterone, high estrogen)
- Hormonal imbalance (low testosterone, high estrogen)
- Hormone changes during puberty or old age
- Some drugs or steroids
- Chronic hepatolith nephrolith thyroid disease
Symptoms of Gynecomastia
Gynecomastia symptoms are generally not difficult to detect. A firm or rubbery lump under the nipple is a common complaint of men and can be accompanied with slight discomfort or tenderness. The swelling may be unilateral or it may involve both breasts. The nipple skin can also be sensitive or swollen. The most severe ones can result in observable chest asymmetry and self-shame.
Common symptoms include:
- Edema in the breast tissue or enlargement
- Pain or sensitivity over the nipple
- A hard lump on one or both of the nipples
- Pain or chest tightness of mild intensity
Diagnosis of Gynecomastia
The diagnosis begins with the physical examination and observation of medical history, to exclude other causes of breast enlargement. Blood tests are frequently ordered by doctors to determine the amount of hormones, liver, and kidney functions. In order to differentiate between gynecomastia and male breast cancer or pseudogynecomastia (fat tissue only), imaging tests such as ultrasound or mammogram can be used. The best treatment plan will be established through early diagnosis.
Diagnostic steps include:
- Breast and abdominal physical examination
- Hormone and liver/kidney blood analysis
- The ultrasound or mammogram imaging
- Taking a history of medication and substances
- Biopsy suspected cancer
When Does Gynecomastia Require Treatment?
Majority of the cases of gynecomastia clear off on its own particularly during puberty. When the condition takes more than 1224 months, and seems to be painful or results in psychological discomfort, it is then necessary to be treated. Chronic or severe ones usually require medical or surgical treatment. A visit to the medical practitioner will aid in determining the cause and suitable treatment.
It is advised to be treated when:
- Pain or tenderness persists
- The size of the breast keeps on growing
- There is mental or emotional agonize
- The hormone levels are very deviant
- The disorder impacts the quality of life
Non-Surgical Treatment Options
Early or mild gynecomastia may be treated without surgical intervention. Doctors can also modify the medications, manage underlying conditions. Lifestyle modifications, such as loss of weight, alcohol intake, and steroids, are helpful as well. Frequent follow-ups would mean the condition is not allowed to progress.
Non-surgical interventions encompass:
- Drug reevaluation and modification
- Hormone therapy ( SERM or aromatase inhibitor)
- Replacement testosterone, in case of low levels
- Weight control and physical activities
Gynecomastia Surgery
Gynecomastia surgery is a long-term fix to conservative methods when the latter do not work. It is also referred to as male breast reduction and eliminates excessive fat and glandular tissue resulting in a flatter chest. Depending on severity, surgeons can opt to employ liposuction, tissues excision, or both. The procedure is safe, effective and the process is usually conducted on outpatient basis.
Gynecomastia surgery types:
- Liposuction: fat burning
- Excision: this is where glandular tissue or skin is cut off
- Combination approach: to use in moderate to severe cases
- Areola repositioning: in late stages
- Outpatient recovery: typically 1- 2 weeks
Recovery After Surgery
There is a quick and easy recovery with the gynecomastia surgery. Majority of the patients are back to light activity in a few days and full activity in 2-3 weeks. Mild swelling, bruising or numbness may also be experienced but they resolve with time. Compression garments assist in shaping the chest and aid in healing. The outcome is seen within nearly no time with a further enhancement after a few months.
Post-surgery recovery tips:
- Wear compression clothes as recommended
- Do not exercise heavily during a period of 2-3 weeks
- Maintain the site of incision to be clean and dry
- Use medication prescribed because of pain or swelling
- Go regularly to follow-ups
This content is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for medical advice. If you’re experiencing any of these symptoms, please contact us for professional help.
Frequently Asked Questions About Gynecomastia
Can Gynecomastia come back after treatment?
Gynecomastia may recur, yes, as long as hormonal imbalance, medications and steroid abuse persist. Prevention of triggers, including a healthy lifestyle, will aid in prevention.
Is Gynecomastia the same as male breast cancer?
Gynecomastia is a harmless (non-cancerous) disorder whereas male breast cancer is uncommon but dangerous. They both can lead to the enlargement of the breast, however, the cancer often presents itself as a hard and non-portable lump.
How can I tell if my breast lump is cancer or Gynecomastia?
Gynecomastia is normally soft and symmetrical at the nipple whereas cancer is hard, irregular and off center. Another one is to always visit the doctor to seek proper evaluation and imaging.
How much does Gynecomastia surgery cost?
Costs vary depending on location and surgical technique.

 Let Us Call You
Let Us Call You











































