BMI (Body Mass Index) is a simple numerical value used to determine whether an individual’s weight is appropriate for their height. It aids in classifying them into underweight, normal weight, overweight and obese. This makes it an effective screening tool for detecting potential health risks such as heart disease or diabetes. The BMI can be calculated manually, and this is done by dividing the weight in kilograms by the height in meters squared. BMI knowledge may be used to make lifestyle adjustments or choose which medical treatment to proceed with.
What is BMI (Body Mass Index)?
BMI (Body Mass Index) is a standard dimension that evaluates the body weight in respect to the height. It is applied worldwide in order to determine the underweight status, healthy weight, overweight and obesity of an individual. Although it does not directly determine the amount of body fat, BMI gives an approximate idea of health risks depending on the standing of weight. Healthcare professionals commonly use it during checkups and preoperative checks. The simplicity of the BMI renders it a helpful and convenient medical and personal tool.
What is my BMI?
Your height and weight are used to calculate your BMI. It also shows whether your present weight is healthy or not depending on your body size. Several online tools, such as BMI calculator men, can help you quickly check your body mass index based on your height and weight.
Why is BMI Important?
The significance of BMI is that it can be determined whether your weight is a danger to your health or not. It serves as a fast guidebook to the doctors and other people to know how the body is composed and make a decision regarding the treatment or the way of life. BMI is particularly important in the pre-surgery period, chronic disease treatment, and weight-reduction monitoring.
Here’s why BMI matters:
- Health risk indicator: BMI is high or low, and there might be such conditions as diabetes, heart disease or malnutrition.
- Operation evaluation: There are a myriad of operations, particularly bariatric and orthopedic operations, with an appropriate bmi level requirement.
- Weight management planning: Aids in developing achievable health objectives.
- Monitoring tool: It is useful for long-term monitoring of weight and overall health progress.
What is BMI Used For?
Body weight divided by height is a common measure of health care that is used to evaluate and to monitor body weight. It is a universal screening tool that assists in realizing that a certain person might be under the threat of weight-related health problems.
Common uses include:
- General health screening: To check whether one is being underweight, normal, overweight, or obese
- Pre-operative tests: Bariatric, orthopedic or spine
- Measuring improvement: In weight loss or fitness
- The data collection used in the design of the study of obesity between populations: Public health data
How Is Body Mass Index (BMI) Calculated?
Body Mass Index (BMI) is a widely used screening tool that estimates body fat by relating weight to height. The standard formula uses weight in kilograms divided by height in meters squared.
- For example, if someone weighs 70 kg and is 1.70 m tall:
- Square the height: 1.70 × 1.70 = 2.89
- Divide weight by that figure: 70 ÷ 2.89 = 24.22
That result is the BMI.
Although it gives a quick estimate, BMI does not distinguish between muscle and fat mass, so it should be interpreted along with other health measures.
Calculating Body Mass Index in Children
The formula used in determining the Body Mass Index (BMI) of children is the same formula as that of adults: weight/height 2, but the manner of interpreting it is different. The results of Pediatric BMI are as compared to standardized growth charts taking into consideration age and sex. According to Centers of Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), the BMI of children is categorized in terms of percentile, but not using definite numbers:
- Underweight: below the 5th percentile
- Healthy weight: 5th to less than 85th percentile
- Overweight: 85th to less than 95th percentile
- Obese: 95th percentile or higher
These charts allow healthcare providers to track growth trends and detect potential health issues early.
Calculating Obesity with Body Mass Index (BMI)
The prevalent definition of obesity in this context is based on the World Health Organization (WHO) global BMI thresholds. Obesity in Turkey has become an increasing public health concern, and BMI is widely used to track and manage weight-related risks across the population.
BMI of 30 or above A BMI of 30 or above indicates obesity. It is further subdivided into:
- Class I (Moderate Obesity): 30–34.9
- Class II (Severe Obesity): 35–39.9
- Class III (Morbid Obesity): 40 and over.
Although BMI is a fast estimate of obesity, clinicians usually use it with waist circumference, fat distribution and metabolism factors to diagnose and assess risks.
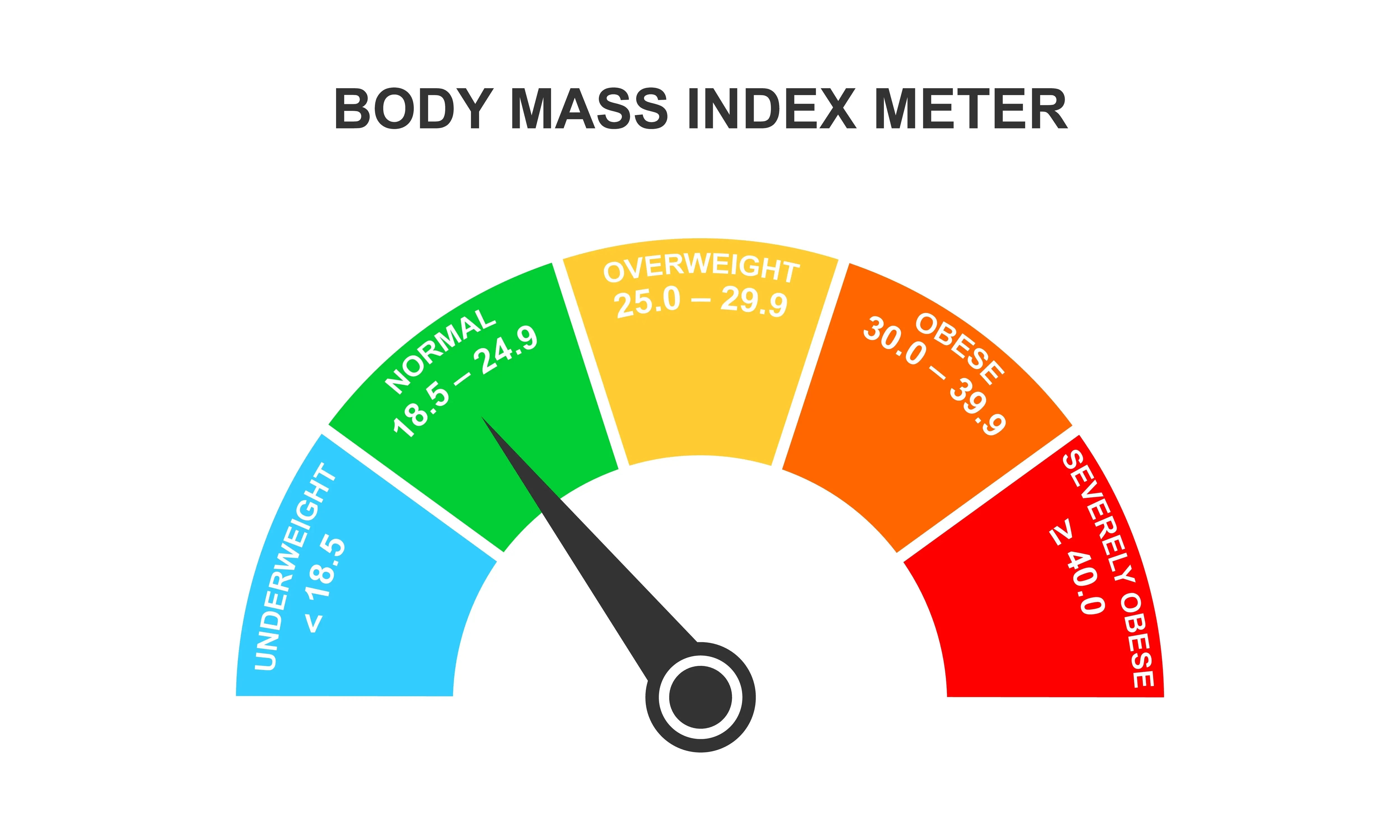
What Are the Body Mass Index Values?
The values of BMI are divided into four main categories which depict the various health statuses:
|
Category |
BMI Range (kg/m²) |
|
Underweight |
Less than 18.5 |
|
Normal weight |
18.5 – 24.9 |
|
Overweight |
25 – 29.9 |
|
Obese |
30 and above |
These categories are used to determine whether an individual’s weight is healthy for their height. Normal BMI will help reduce chronic diseases and enhance metabolic health.
How Is the Body Mass Index Classification Evaluated?
The classification of BMI is compared to the available medical categories and measured by comparing the resultant value of the calculated BMI. In adult cases, definite numerical values are taken, but in children, age- and sex-specific percentiles are considered.
But, the BMI does not assess the body fat percentage or muscle mass hence healthcare providers use it with other measurements such as waist-to-hip ratio or body composition scans as a complete health assessment.
This content is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. If you are experiencing any of the mentioned symptoms, please fill out the form to contact us for professional support.
Frequently Asked Questions About BMI (Body Mass Index)
What health risks can be ıdentified through body mass index?
High BMI exposes a person to the possibility of heart disease, diabetes, stroke, and even some forms of cancer; a very small BMI could also be a sign of malnutrition or the lack of nutrients.
Why is BMI important before surgery?
Surgeons rely on BMI to determine the risk of anesthesia and potential complications during surgical procedures because both excessive and too low values of BMI may influence the wound healing and recovery process.
Is BMI an accurate measure of health?
BMI measures the amount of fat in the body but does not consider the muscle, bone or fat distribution and thus it ought to be applied with another health measure.
What happens if my BMI is too high for surgery?
When BMI is higher than the safe levels, surgeons can suggest weight loss or preoperative conditioning to minimize the complications during and after surgery.
Does body mass ındex differ by gender?
The formula used in calculating the BMI is applicable whether one is a man or a woman but there are natural variations of fat distribution and muscle mass that can influence interpretation.
What should be done to lower body mass index?
BMI can be safely and sustainably reduced by maintaining a calorie deficit through a balanced diet, regular exercise, and healthy lifestyle changes.
Is measuring body mass index alone sufficient?
BMI is a measuring instrument; other tests such as waist circumference, cholesterol and blood sugar tests will give a more definite health profile.
Does exercise affect body mass index?
Yes, with regular physical exercise, one can reduce body fat and build muscle mass, resulting in a healthier BMI and overall fitness.

 Let Us Call You
Let Us Call You





















